Fantastic reflections @lucas10mauriz …
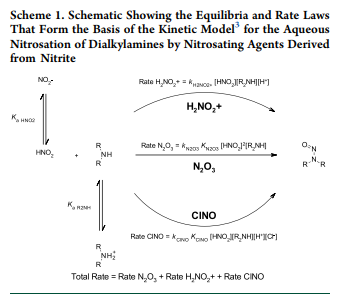
I would like to expand to call attention to Dr. Justin Moser presentation about using model amine systems to study the potential formation in oral solid dosage, some on his work was published back in May 2023
The data presented on the models proved that they could be used to estimate the formation of nitrosamines that may form via dialkyl amines (vulnerable amines). Using data such as Vulnerable amine molecular weight (MW), pKa, dose, dose/day, formulation %s, and Nitritie content; one can predict the formation of particular nitrosamines over the shelf life of the dosage form. Futhermore, the mode was designed to over-predict nitrosamines formation, where HNO2 degradation was ignored.
Details of the modeling can be found in the Ashworth et all publication.