Dear colleagues,
I would like to pose a question regarding the use of Fluconazole. From what I have seen and researched about its structure, this compound contains two triazole groups that have the potential to react and form N-nitroso Fluconazole. My question is whether the formation of N-nitroso Fluconazole is a result of degradation of the molecule or a metabolic process to separate the triazole groups.
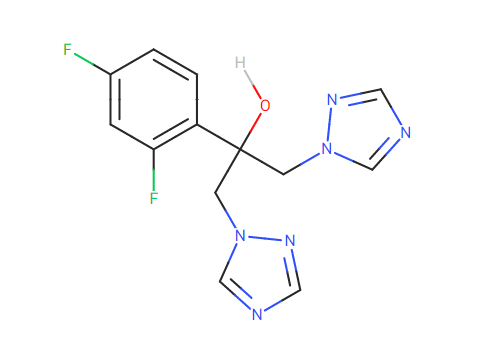
Fluconazole
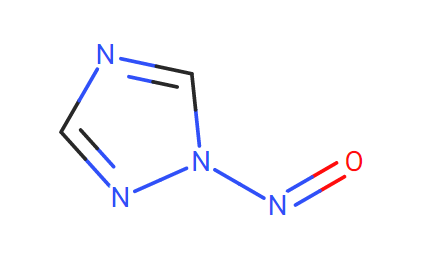
N-nitroso Fluconazole
I appreciate any insights or experiences you may have regarding this topic. Thank you for your participation and contribution to the discussion.
All the best,
Christian Romo
2 Likes
Hi @CMRomo.
I understand fluconazole has minimal metabolism in liver and moreover, it inhibits the main CYP enzymes CYP2C19, CYP2C9, and CYP3A4. Most of fluconazole remains unchanged when administered into body. So, i doubt formation from metabolic process with triazole ring.
Hi @Pradpharma,
Thank you for your response and insights regarding fluconazole metabolism and its potential for N-nitroso Fluconazole formation. Your explanation about the minimal metabolism of fluconazole in the liver and its inhibitory effects on key CYP enzymes is helpful in understanding its stability in the body. Based on this information, it is reasonable to question whether N-nitroso Fluconazole formation occurs through a metabolic process involving the triazole ring, or via another pathway.
Given this context, I would like to further inquire about the community’s thoughts on the conditions or scenarios under which N-nitroso Fluconazole could potentially form. Are there any specific factors, such as environmental conditions or interactions with other substances, that you believe could contribute to the formation of N-nitroso Fluconazole despite its metabolic stability?
Thank you again for your contribution, and I look forward to your insights on this matter.
Best regards,
Christian Romo
Hi @CMRomo ,
I could say that here, we need to divide the scenario in two:
For the first one, the answer is already indicated by our colleague. Now regarding the formation of a Nitroso-triazole (1-Nitroso-1,2,4-Triazole) I think first is more possible a C-nitrosation or nitration than anything else first.
- In major synthesis suppliers it is already discontinued the material. I wonder that it was not actually possible to synthetize the material. Product Page (tlcstandards.com)
Any similar nitroso-triazole linked to the rest of Fluconazole molecule also seem very hard to generate. Finally, a “nitroso"triazole” cant undergo alpha hydroxylation meaning can be a Non of concern nitrosamine. I wonder more if to form the triazole rings any nitrite salt was used, that could react w/ any other amine source elsewhere in the formula.
2 Likes
Dear @Diego_HM,
Thank you sincerely for your valuable response and insights regarding the formation of N-nitroso triazole. Your contributions have shed light on potential mechanisms, including the possibility of C-nitrosation or nitration, as well as the discontinued status of related materials in major synthesis suppliers. Your mention of the use of nitrite salts and their reaction with other amine sources also brings an interesting perspective to the discussion.
Once again, I thank you for your valuable input and contributions.
Best regards,
1 Like

