Thanks @mflorea. Including the abstract for reference…
Abstract
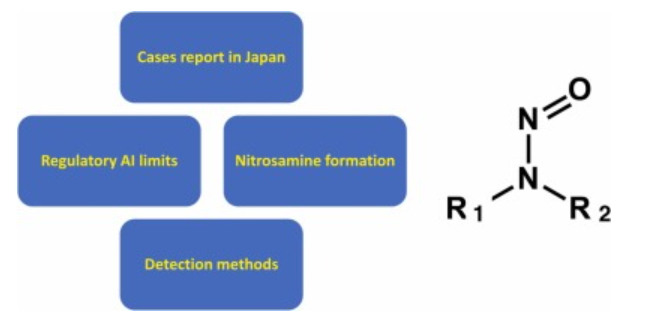
In recent years, mutagenic nitrosamines, such as N-nitrosodimethylamine, have been detected in medicine. This has led to global product recalls and long-term supply suspensions by pharmaceutical companies and consequent clinical impacts. Measures to control nitrosamines in medicine, including detection methods and clarification of contamination routes, are being implemented worldwide. In this review, we focus on case reports of nitrosamine contamination of drug products in Japan, nitrosamine formation mechanisms during manufacturing and storage, as well as detection methods. We also discuss the acceptable nitrosamine intake (ng/day) in chemically synthesized drug substances in human drugs (including drug products) in the US, EU, and Japan. Overall, nitrosamine contamination of medicines is expected to remain a global public health issue. Therefore, detection methods using new technologies and detailed analysis of the formation mechanisms are necessary. However, excessive regulation may cause essential drug shortages owing to product recall; therefore, a realistic and prudent response based on regulatory science is needed.