Except for the guidance, there are some official/unofficial surrogates for the read-across method in this Nitrosamine Exchange. I will pick them up for your practice. Please keep in mind that not all of them are correct.
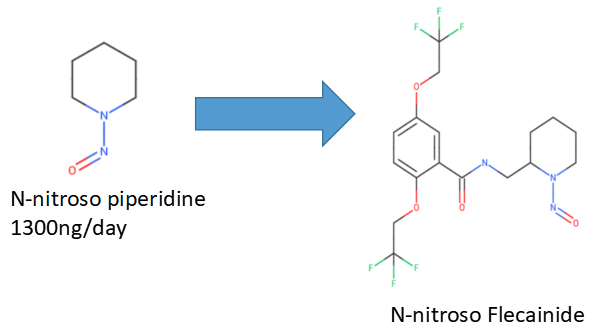
Except for the guidance, there are some official/unofficial surrogates for the read-across method in this Nitrosamine Exchange. I will pick them up for your practice. Please keep in mind that not all of them are correct.

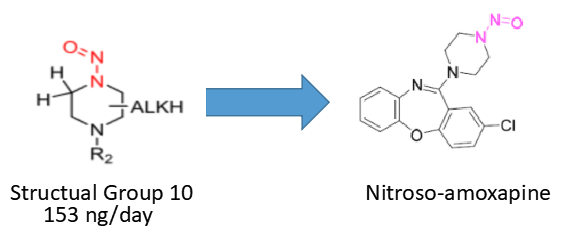
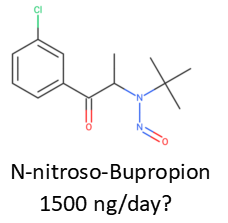
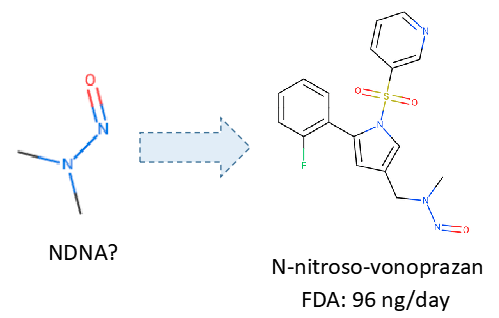
I think is a good approach. I belive You’ve used this publication to establish AI’s? https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00369
Thank you for asking, @1nsekt. We’ve used it for beta-blocker and amoxapine. And Ministry of Health, Labour and. Welfare, Japan accepted the AI calculated by the strategy you referred to at amoxapine. The risk assessment report of amoxapine translated into English by DeepL translate is as follows;
001004627 en-US.pdf (600.5 KB)
Looking for a direct structural similarity seems to always be the best approach.
However, methods presented by LHASA, i.e. the categorization of nitrosamines according to the groups nearby to nitrosoamine and assigning the appropriate effect on TD50 would be more universal https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.2c00199 (and his previous paper Developing structure-activity relationships for N-nitrosamine activity - ScienceDirect).
However, the original approach, i.e. converting the molar mass, seems to be inapplicable, as some cases differ greatly - especially the benzyl, ethyl and methyl derivatives of nitrosamines, which are far more potent carcinogens.